Tutorial
In this tutorial we're going to learn how to install and configure from scratch IOTConnect in a RaspberryPi Zero W to read OBDII data from a Hyundai Ioniq EV 28kWh and the GPS position and publish to a MQTT broker.
Needed Hardware
- Raspberry Pi Zero W
- LTE Stick Huawei E3372
- ELM327 Bluetooth scanner
- USB car charger
- USB GPS receiver GlobalSat BU-353-S4
- USB cable extender
- USB to Micro USB adapter
- USB OTG cable
- Raspberry Pi Zero case
- Velcro stickers
See the Amazon wishlist.
Install the OS
If you are new to Raspberry Pi, you should get some information about it here.
If you are already familiar with the Raspberry Pi, let's start.
The code and the following procedure has been designed and tested to use the Raspberry Pi OS (previously called Raspbian).
Use Raspberry Pi Imager for an easy way to install Raspberry Pi OS (and other operating systems) to an SD card.
Once you have Raspberry Pi Imager installed open it and:
- Under
Choose OSoption selectRaspberry Pi OS (other)and then chooseRaspberry Pi OS Lite (32-bit) - Choose your SD card
- and Write it
WLAN and SSH configuration
Before you can put the SD card into the Pi and boot it, you should enable SSH connections and configure the WLAN.
To enable ssh create an empty file called ssh in the root of your SD card.
To configure WLAN create a file “wpa_supplicant.conf” with the following content and copy it in the root of your SD card.
I recommend to configure both your Home and Car WiFi in this step
country=ES
ctrl_interface=DIR=/var/run/wpa_supplicant GROUP=netdev
update_config=1
network={
ssid="<YOUR HOME WLAN SSID HERE>"
psk="<YOUR HOME WLAN PASSWORD HERE>"
priority=20
key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
id_str="home"
}
network={
ssid="<YOUR CAR WLAN SSID HERE>"
psk="<YOUR CAR WLAN PASSWORD HERE>"
priority=1
key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
id_str="car"
}
First Raspberry Pi startup
To be able to easily ssh your Pi, I recommend that you set up your home router to assign a static IP address to the Raspberry Pi. As the procedure is different for every router, please google for some information on how to do it on your router.
Once you have set up your IP address, turn on your Raspberry Pi and use any SSH client to connect to it.
The default username is pi the password raspberry.
Change the default password by typing: passwd.
Run raspi-config to Enable wait for network a boot (you may also want to change other settings such as Locale, Time Zone,...):
- Type:
sudo raspi-config. - Scroll down to
3 Boot Optionsand press enter. - Scroll down to
B2 Wait for Network at Bootand press enter. - Select
YES
This tells the Raspberry Pi to wait for a network during the boot process.
Save and exit the raspi-config by selecting OK and then Finish. Then, reboot your Pi. Now your Pi should wait for a network before completely booting! BTW: Yes, this works with WiFi.
Package intallation
Get the latest updates from the OS (this may take a while, so relax, grab a beer and enjoy looking at the progress...)
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
Reboot if needed.
sudo reboot
Then install needed packages:
sudo apt-get install bluetooth bluez-tools blueman python3-pip git
Pairing OBDII Bluetooth Dongle with Raspberry Pi
Now we're ready to pair the OBDII Bluetooth Dongle with Raspberry Pi.
IMPORTANT Bellow requirements need to be met to pair the OBDII bluetooth with the Raspberry Pi:
- OBDII dongle is plugged into the OBDII port of your car.
- Raspberry Pi is within the range of the OBDII bluetooth dongle (~<5m).
- Raspberry Pi is connected to the WiFi and accessible through ssh. During the pairing process, I use a powerbank to power the Raspberry Pi to keep it within the range of OBDII bluetooth and my home WiFi. In my case using the USB charger plugged into the car makes the RaspberryPi to be out of WiFi range.
- The vehicle is switched on.
I'm lucky and meeting all those requirements is easy for me!!!. If are not so lucky, you will need to find an alternative way pair the OBDII with the Raspberry Pi.
Ok, so now we're ready to start the pairing process:
sudo bluetoothctl
Then when the [bluetooth]# promt is shown, type:
agent on
scan on
You will get a list of all Bluetooth devices in range and within the list it should also appear your OBDII dongle. Identify it and you will also see the device address (Format: XX: XX: XX: XX: XX: XX). Note down this address because it's important for the next steps!.
Please replace XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX with the address of your OBDII dongle for next steps.
Pairing:
pair XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
Now you have to enter the device code. Usually it's 1234 or 0000, see your OBDII instructions manual to find your device code.
If that worked, you still have to trust the device, so you don't need to pair the device every time:
trust XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
To be able to access the OBDII dongle, it must be integrated as a serial device. This needs to be done after each restart.
To create your OBDII dongle as a serial device, add the following line to the file /etc/rc.local:
sudo rfcomm bind hci0 XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX 1
Then reboot the Raspberry Pi
sudo reboot
Configuring the GPS
Install needed packages:
sudo apt-get install gpsd gpsd-clients ntp
Now configure the gpsd daemon:
sudo nano /etc/default/gpsd
The file should look something like this (I only needed to change the DEVICES property):
# Default settings for the gpsd init script and the hotplug wrapper.
# Start the gpsd daemon automatically at boot time
START_DAEMON="true"
# Use USB hotplugging to add new USB devices automatically to the daemon
USBAUTO="true"
# Devices gpsd should collect to at boot time.
# They need to be read/writeable, either by user gpsd or the group dialout.
DEVICES="/dev/ttyUSB0"
# Other options you want to pass to gpsd
GPSD_OPTIONS=""
And then restart the service.
sudo systemctl restart gpsd
To test that GPS is working, first make sure you have the GPS USB device plugged into your Raspberry Pi USB port (you will need the USB to micro USB adapter) and run cgps utility.
cgps
You should see something like:
lqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqklqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqk
x Time: 2020-07-01T17:03:30.000Z xxPRN: Elev: Azim: SNR: Used: x
x Latitude: x.xxxxxxxxx N xx 1 67 078 47 Y x
x Longitude: y.yyyyyyyy E xx 3 74 321 32 Y x
x Altitude: 124.967 m xx 4 37 183 19 Y x
x Speed: 0.00 kph xx 8 12 165 24 Y x
x Heading: 0.0 deg (true) xx 11 43 138 44 Y x
x Climb: 0.00 m/min xx 14 24 045 40 Y x
x Status: 3D DIFF FIX (6 secs) xx 17 34 309 26 Y x
x Longitude Err: +/- 10 m xx 19 15 319 27 Y x
x Latitude Err: +/- 4 m xx 22 66 034 39 Y x
x Altitude Err: +/- 19 m xx 28 13 264 22 Y x
x Course Err: n/a xx 31 10 079 27 Y x
x Speed Err: +/- 72 kph xx 123 35 138 43 Y x
x Time offset: 1.264 xx x
x Grid Square: JM19ip xx x
mqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqjmqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqj
#precedence ::ffff:0:0/96 100
#
# scopev4 <mask> <value>
# Add another rule to the RFC 6724 scope table for IPv4 addresses.
# By default the scope IDs described in section 3.2 in RFC 6724 are
# used. Changing these defaults should hardly ever be necessary.
# The defaults are equivalent to:
#
#scopev4 ::ffff:169.254.0.0/112 2
#scopev4 ::ffff:127.0.0.0/104 2
#scopev4 ::ffff:0.0.0.0/96 14
Mobility Support for IPv6 [RFC3775]
udplite 136 UDPLite # UDP-Lite [RFC3828]
mpls-in-ip 137 MPLS-in-IP # MPLS-in-IP [RFC4023]
manet 138 # MANET Protocols [RFC5498]
hip 139 HIP # Host Identity Protocol
shim6 140 Shim6 # Shim6 Protocol [RFC5533]
wesp 141 WESP # Wrapped Encapsulating Security Payload
rohc 142 ROHC # Robust Header Compression
H.10- 04/25/2019 115","activated":"2020-07-01T17:03:24.423Z","flags":1,"native":1,"bps":4800,"parity":"N","stopbits":1,"cycle":1.00}]}
{"class":"WATCH","enable":true,"json":true,"nmea":false,"raw":0,"scaled":false,"timing":false,"split24":false,"pps":false}
{"class":"TPV","device":"/dev/ttyUSB0","status":2,"mode":3,"time":"2020-07-01T17:03:24.000Z","ept":0.005,"lat":x.xxxxxxxxxxx,"lon":y.yyyyyyyyyyyy,"alt":124.967,"epx":10.106,"epy":4.597,"epv":19.127,"track":0.0000,"speed":0.000,"climb":0.000,
"eps":20.21,"epc":38.25}
If you are not getting GPS coordinates something may be wrong. Please google for additional information and troubleshooting.
Wiring
- ELM327 Bluetooth scanner should be plugged into the OBDII port of your car.
- USB car charger should be plugged into the 12V plug of your car.
- LTE Stick Huawei E3372 should be plugged into the USB car charger (you may want to use the USB cable extender to hide a bit the stick).
- Raspberry Pi Zero W should be plugged into the USB car charger using the USB to Micro USB adapter.
- USB GPS receiver GlobalSat BU-353-S4 should be plugged to the Raspberry Pi using the USB OTG cable.
Installing IOTConnect
Follow the installation instructions from the Getting started page.
Prepare config files
Make sure you are in /opt/IOTConnect folder.
Copy config file from template.
cp iotconnect/iotconnect.config.template.json iotconnect/iotconnect.config.json
Adapt it to your needs.
Execute the script
To test that everything works, execute IOTConnect:
- Make sure all the wiring is properly done (see Wiring section above).
- The vehicle is switched on.
- The Raspberry Pi is in range of OBDII bluetooth.
Run the command:
python3 -m iotconnect
This should publish the information to the configured destination.
If this works congratulations you are almost done!
Run as a service
Follow the run as a service instructions from Getting started page.
Car WiFi
To have WiFi in the car, I use a UBS powered stick that as soon as it get some power it startup, connects to the 4G LTE network and operates as a WiFi router. In my case I use the Huawei E3372 LTE stick. Please refer to your specific stick instructions on how to configure it.
Data types and data format
Those are the MQTT topics and format used for each one:
state
This information may be useful to know that the script is running and last time it ran. State topic is published from IoniqEVMonitor in the config['mqtt']['topic_prefix']state i.e.: car/sensor/ioniq/state as a JSON object with the following format:
{
timestamp integer Linux Epoch time.
state string Constant string with the "running" value.
monitors array Array containing all the configured monitors and their status (started or stopped).
}
Sample:
{
"timestamp": 1597091185,
"state": "running",
"monitors": [{"GpsMonitor": "started"}, {"IoniqEVMonitor": "started"}]}
}
battery
BMS (Battery Management System) information is published from IoniqEVMonitor in the config['mqtt']['topic_prefix']battery i.e.: car/sensor/ioniq/battery as a JSON object with the following format:
{
timestamp integer Linux Epoch time.
socBms float (0-100) Battery status of charge in % (as seen by Battery Management System).
socDisplay integer (0-100) Battery status of charge in % (as seen as in car display).
soh float (0-100) Battery status of health in %.
bmsIgnition 0 or 1 Car ignition. 0: false, 1: true.
bmsMainRelay 0 or 1 BMS main relay. 0: false, 1: true.
auxBatteryVoltage float Aux battery voltage in V.
auxBatteryPercent float Aux battery percentaje.
charging 0 or 1 Is the car charging ? 0: false, 1: true.
normalChargePort 0 or 1 Is charging using normal charge port? 0: false, 1: true.
rapidChargePort 0 or 1 Is charging using rapid charge port? 0: false, 1: true.
minsToCompleteCharge integer Minutes to complete 100% battery charge. Estimation based on current charge speed. 0 if not charging.
fanStatus integer (0-9) Cooling fan speed. 0 means stopped. 1 to 9 lower to higher speed.
fanFeedback integer Fan feedback signal in Hz.
cumulativeEnergyCharged float Cumulative energy charged in kWh.
cumulativeEnergyDischarged float Cumulative energy discharged in kWh.
cumulativeChargeCurrent float Cumulative current charged in A.
cumulativeDischargeCurrent float Cumulative current discharged in A.
availableChargePower float Available charge power kW. In Ioniq EV max value is 98kW.
availableDischargePower float Available discharge power in kW. In Ioniq EV max value is 98kW.
dcBatteryCellVoltageDeviation integer DC battery cell voltage deviation in V.
dcBatteryHeater1Temperature float DC battery heater1 temperature in ºC.
dcBatteryHeater2Temperature float DC battery heater2 temperature in ºC.
dcBatteryInletTemperature integer DC battery inlet temperature in ºC.
dcBatteryMaxTemperature integer DC battery maximum cell temperature in ºC.
dcBatteryMinTemperature integer DC battery minimum cell temperature in ºC.
dcBatteryAvgTemperature integer DC battery average cells temperature in ºC.
dcBatteryCellMaxVoltage float DC battery maximum voltage in V.
dcBatteryCellNoMaxVoltage integer (1-96) DC battery maximum voltage cell number.
dcBatteryCellMaxDeterioration float (0-100) DC battery maximum deterioration cell in %.
dcBatteryCellNoMaxDeterioration integer (1-96) DC battery maximium deterioration cell number.
dcBatteryCellMinVoltage float DC battery minimum voltage in V.
dcBatteryCellNoMinVoltage integer (1-96) DC battery minimum voltage cell number.
dcBatteryCellMinDeterioration float (0-100) DC battery minimum deterioration cell in %.
dcBatteryCellNoMinDeterioration integer (1-96) DC battery minimum deterioration cell number.
dcBatteryCurrent float DC battery instant current in A.
dcBatteryPower float DC battery instant power in kW.
dcBatteryVoltage float DC battery instant voltage in V.
dcBatteryModuleTempxx float DC battery module temperature in ºC. Where xx goes from 01 to 12.
dcBatteryCellVoltagexx float DC battery cell voltage in V. Where xx goes from 01 to 96.
driveMotorSpeed integer Motor speed in RPM.
}
Sample:
{
"timestamp":1594794497,
"socBms":45.0,
"socDisplay":46,
"soh":100.0,
"bmsIgnition": 1,
"bmsMainRelay": 1,
"auxBatteryVoltage":14.5,
"auxBatteryPercent":50.0,
"charging":0,
"normalChargePort":0,
"rapidChargePort":0,
"minsToCompleteCharge": 0,
"fanStatus":0,
"fanFeedback":0,
"cumulativeEnergyCharged":3029.8,
"cumulativeEnergyDischarged":2952.3,
"cumulativeChargeCurrent":8400.0,
"cumulativeDischargeCurrent":8372.3,
"availableChargePower":98.0,
"availableDischargePower":98.0,
"dcBatteryCellVoltageDeviation": 0,
"dcBatteryHeater2Temperature": 0.0,
"dcBatteryHeater1Temperature": 0.0,
"dcBatteryInletTemperature":27,
"dcBatteryMaxTemperature":28,
"dcBatteryMinTemperature":26,
"dcBatteryAvgTemperature":27,
"dcBatteryCellMaxDeterioration": 0,
"dcBatteryCellNoMaxDeterioration": 2,
"dcBatteryCellMinDeterioration": 100.0,
"dcBatteryCellNoMinDeterioration": 10,
"dcBatteryCurrent":1.7,
"dcBatteryPower":0.5924499999999999,
"dcBatteryVoltage":348.5,
"dcBatteryModuleTemp01":27.0,
"dcBatteryModuleTemp02":27.0,
"dcBatteryModuleTemp03":26.0,
"dcBatteryModuleTemp04":27.0,
"dcBatteryModuleTemp05":27.0,
"dcBatteryModuleTemp06":27.0,
"dcBatteryModuleTemp07":27.0,
"dcBatteryModuleTemp08":28.0,
"dcBatteryModuleTemp09":27.0,
"dcBatteryModuleTemp10":27.0,
"dcBatteryModuleTemp11":27.0,
"dcBatteryModuleTemp12":27.0,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage01":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage02":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage03":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage04":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage05":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage06":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage07":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage08":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage09":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage10":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage11":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage12":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage13":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage14":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage15":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage16":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage17":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage18":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage19":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage20":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage21":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage22":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage23":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage24":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage25":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage26":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage27":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage28":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage29":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage30":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage31":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage32":3.62,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage33":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage34":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage35":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage36":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage37":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage38":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage39":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage40":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage41":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage42":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage43":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage44":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage45":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage46":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage47":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage48":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage49":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage50":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage51":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage52":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage53":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage54":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage55":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage56":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage57":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage58":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage59":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage60":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage61":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage62":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage63":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage64":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage65":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage66":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage67":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage68":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage69":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage70":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage71":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage72":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage73":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage74":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage75":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage76":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage77":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage78":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage79":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage80":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage81":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage82":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage83":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage84":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage85":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage86":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage87":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage88":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage89":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage90":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage91":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage92":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage93":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage94":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage95":3.6,
"dcBatteryCellVoltage96":3.6,
"driveMotorSpeed":4200
}
odometer
Odometer information is published from IoniqEVMonitor in the config['mqtt']['topic_prefix']odometer i.e.: car/sensor/ioniq/odometer as a json object with the following format:
{
timestamp integer Linux Epoch time.
odometer integer Odometer value in Km.
}
Sample:
{
"timestamp": 1596316222,
"odometer": 23100
}
vmcu
Vehicle Motor Control Unit information is published from IoniqEVMonitor in the config['mqtt']['topic_prefix']vmcu i.e.: car/sensor/ioniq/vmcu as a json object with the following format:
{
timestamp integer Linux Epoch time.
vin string Vehicle Identification Number, also called a chassis number (or número de bastidor in spanish).
gear string Gear stick position. P = Park, N = Neutral, D = Drive or R = Rear.
speed float Vehicle speed in kmh.
accel_pedal_depth integer Accelerator pedal depth in %.
brake_lamp 0 or 1 0 brake lamp is off, 1 brake lamp is on.
brakes_on 0 or 1 0 brakes are off, 1 brakes are on.
auxBatteryCurrent float Aux battery current in A. PENDING TO VERIFY THAT IS CORRECT!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
}
Sample:
{
"timestamp":1594994497,
"vin":"XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX",
"gear": "D",
"speed": 67.0,
"accel_pedal_depth": 28,
"brake_lamp": 0,
"brakes_on": 0,
"auxBatteryCurrent": -0.052
}
tpms
Tire Pressure Monitor System information is published from IoniqEVMonitor in the config['mqtt']['topic_prefix']tpms i.e.: car/sensor/ioniq/tpms as a json object with the following format:
{
timestamp integer Linux Epoch time.
tire_fl_pressure float Front left tire pressure in bar.
tire_fl_temperature integer Front left tire temperature in ºC.
tire_fr_pressure float Front right tire pressure in bar.
tire_fr_temperature integer Front right tire temperature in ºC.
tire_bl_pressure float Back left tire pressure in bar.
tire_bl_temperature integer Back left tire temperature in ºC.
tire_br_pressure float Back right tire pressure in bar.
tire_br_temperature integer Back right tire temperature in ºC.
}
Sample:
{
"timestamp":1596146085,
"tire_fl_pressure":2.7,
"tire_fl_temperature":28,
"tire_fr_pressure":2.6
"tire_fr_temperature":28,
"tire_bl_pressure":2.6,
"tire_bl_temperature":33,
"tire_br_pressure":2.5,
"tire_br_temperature":33
}
external temperature
External temperature information is published from IoniqEVMonitor in the config['mqtt']['topic_prefix']ext_temp i.e.: car/sensor/ioniq/ext_temp as a json object with the following format:
{
timestamp integer Linux Epoch time.
external_temperature float External temperature in ºC.
}
Sample:
{
"timestamp": 1596316222,
"external_temperature": 29.5
}
location
Location information is published from GpsMonitor in the config['mqtt']['topic_prefix']location i.e.: car/sensor/ioniq/location as a JSON object with the following format:
{
latitude float Latitude.
longitude float Longitude.
last_update float Linux Epoch time.
gps_accuracy float Max of latitude or longitude estimated error.
platitude float Latitude fixed on last iteration.
plongitude float Longitude fixed on last iteration.
track float Course over ground in degrees from True North.
speed float Speed in m/s.
epx float Estimated longitude error.
epy float Estimated latitude error.
epv float Estimated altitude error.
ept float Estimated time error.
eps float Estimated Speed error.
mode float NMEA mode; values are: 0 - NA, 1 - No Fix, 2D and 3D.
climb float Climb (Positive) or Sink (Negative) rate in m/s of upwards or downwards movement.
}
Sample:
{
"track":326.4788,
"platitude":19.634422362,
"speed":0.216,
"epx":9.772,
"epy":15.465,
"epv":30.186,
"ept":0.005,
"eps":30.93,
"longitude":23.23253151,
"last_update":1593980780,
"gps_accuracy":15.465,
"mode":3,
"latitude":19.644422362,
"climb":-0.021,
"plongitude":23.24253151
}
Monitor when charging
One of the caveats of using the existing 12V plugs is that those are only powered when the car engine is on, meaning that it's not possible to monitor the status of the battery while the car is charging.
To be able to monitor the battery while the car is charging and not drain the 12V battery I've added a new 12V plug that takes the power from the fuse box that it's ONLY active when the car engine is on or the car is charging.
You can use the following fuse (IG3 2) to achieve this:
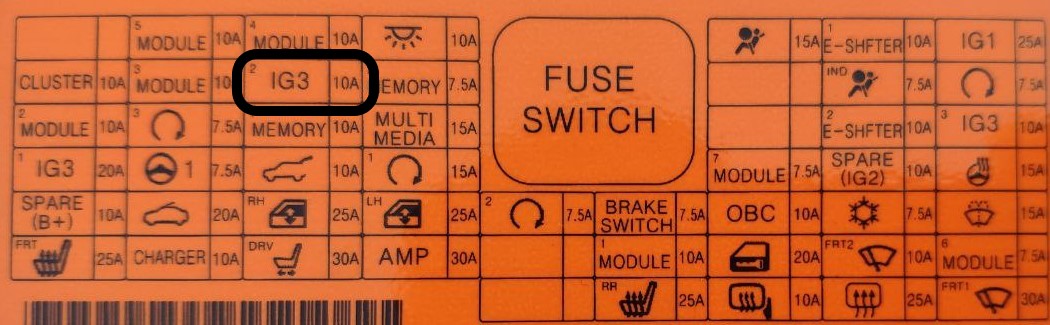
In order to make it easy to take the power from the fuse box I've used the following adaptor.
Online log management tool - Logtail installation
As the Raspberry Pi will usually run in your car's WiFi it is going to be complex for you to debug problems or even look at the log files. For that I'm using a Log Management tool in the cloud that offers a free tier that is more than enough for the purpose of this project (1 GB/month and 3 days log retention).
Just create a free account in Logtail create a Python source, and copy & paste your Source token to the Logtail handler in logging.conf file.